Shell and tube heat exchanger structure type, heat transfer mechanism, design points
The shell and tube heat exchanger is composed of shell, heat transfer tube bundle, tube sheet, baffle (baffle) and tube box and other components. The shell is mostly cylindrical, with a tube bundle inside, and the two ends of the tube bundle are fixed on the tube sheet.
There are two kinds of hot and cold fluids for heat exchange, one flows inside the tube, called tube-side fluid; the other flows outside the tube, called shell-side fluid. In order to improve the heat transfer partial coefficient of the fluid outside the tube, several baffles are usually installed in the shell.
The baffle can increase the velocity of the shell-side fluid, forcing the fluid to pass through the tube bundle multiple times according to the specified distance, and enhance the degree of fluid turbulence.
The heat exchange tubes can be arranged in equilateral triangles or squares on the tube sheet. The arrangement of equilateral triangles is more compact, the degree of turbulence of the fluid outside the tube is high, and the heat transfer coefficient is large; the arrangement of squares makes it easy to clean the outside of the tube, and is suitable for fluids that are prone to fouling.
Every time the fluid passes through the tube bundle is called a tube pass; every time the fluid passes through the shell is called a shell pass. The picture shows the simplest single-shell-side single-tube heat exchanger, referred to as 1-1 type heat exchanger. In order to increase the velocity of the fluid in the tube, dividers can be installed in the tube boxes at both ends to divide all the tubes into several groups.
In this way, the fluid only passes through part of the tubes at a time, so it goes back and forth multiple times in the tube bundle, which is called multi-tube pass. Similarly, in order to increase the flow rate outside the tube, longitudinal baffles can also be installed in the shell to force the fluid to pass through the shell space multiple times, which is called multi-shell pass. Multi-tube and multi-shell can be used together.
Because the temperature of the fluid inside and outside the tube is different in the shell-and-tube heat exchanger, the temperature of the shell and the tube bundle of the heat exchanger is also different. If there is a large difference between the two temperatures, a large thermal stress will be generated in the heat exchanger, causing the tube to bend, break, or pull off the tube sheet.
Therefore, when the temperature difference between the tube bundle and the shell exceeds 50°C, appropriate compensation measures should be taken to eliminate or reduce thermal stress. According to the compensation measures adopted, shell and tube heat exchangers can be divided into the following main types:
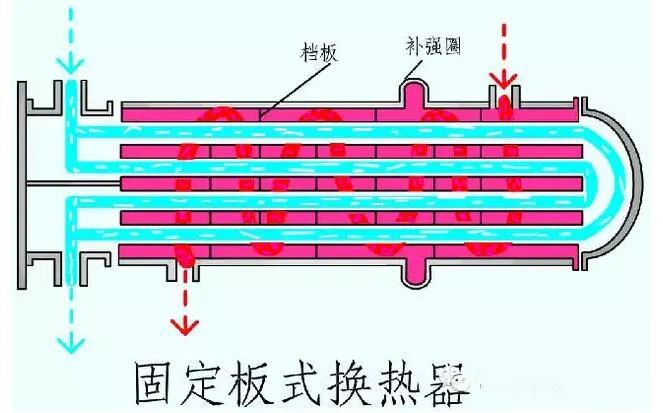
①The tube sheets at both ends of the tube bundle of the fixed tube-sheet heat exchanger are integrated with the shell. The structure is simple, but it is only suitable for heat exchange operations when the temperature difference between the hot and cold fluids is not large and the shell side does not need mechanical cleaning. When the temperature difference is slightly large and the shell side pressure is not too high, an elastic compensation ring can be installed on the shell to reduce thermal stress.
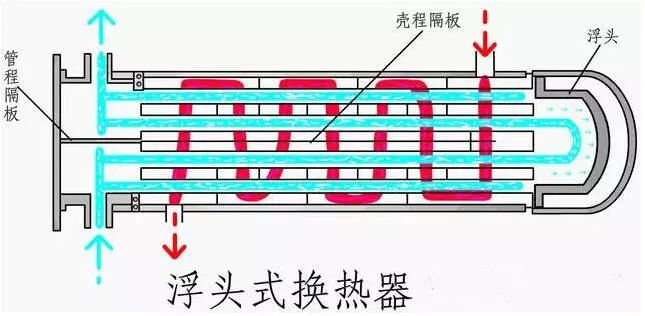
②The tube plate at one end of the tube bundle of the floating head heat exchanger can float freely, completely eliminating thermal stress; and the whole tube bundle can be pulled out from the shell, which is convenient for mechanical cleaning and maintenance. Floating head heat exchangers are widely used, but the structure is more complicated and the cost is higher.
③ In the U-shaped tube heat exchanger, each heat exchange tube is bent into a U shape, and the two ends are respectively fixed on the upper and lower areas of the same tube plate. This kind of heat exchanger completely eliminates thermal stress, and its structure is simpler than that of the floating head type, but the tube side is not easy to clean.
④Stuffing box heat exchanger The structural feature of the stuffing box heat exchanger is that only one end of the tube sheet is fixedly connected to the shell, and the other end is sealed with a stuffing box. The tube bundle can expand and contract freely, and there will be no temperature difference stress caused by the temperature difference between the shell wall and the tube wall.
The advantage of the stuffing box heat exchanger is that it is simpler in structure than the floating head heat exchanger, easy to manufacture, less consumables, and low in cost; the tube bundle can be drawn out from the shell, and both inside and between the tubes can be cleaned, which is convenient for maintenance. Its disadvantage is that the pressure resistance of the stuffing box is not high, generally less than 4.0MPa;
The shell-side medium may leak through the stuffing box, which is not suitable for flammable, explosive, toxic and expensive media. The stuffing box heat exchanger is suitable for the occasions where the temperature difference between the tube and the shell wall is large or the medium is easy to scale, and needs to be cleaned frequently and the pressure is not high.
⑤ Kettle heat exchanger The structural feature of the kettle heat exchanger is that an appropriate evaporation space is set on the upper part of the shell, and it also functions as a steam chamber.
Tube bundles can be fixed tubesheet, floating head or U-tube. The kettle heat exchanger is easy to clean and maintain, can handle unclean and easily fouled media, and can withstand high temperature and high pressure. It is suitable for liquid-vapor heat exchange and can be used as a waste heat boiler with the simplest structure.
HEAD OFFICE:Yingcheng East Road, Ganjingzi District, Dalian, China. Tell/Fax: +86-411-66322221 Web: www.smartcold.tech Email: sales@smartcold.tech |  |
SHANDONG BRANCH:Room 3162, Building 3, No.9 Gangxing Road, Jinan, China. Tell/Fax: +86-531-89263325 Web: www.smartcoldtech.com |  |
ZHEJIANG OFFICE:Rm501, No.69, Futian 2nd District, Yiwu, China. Tell/Fax: +86-539-86858841 Online shop: |  |



















